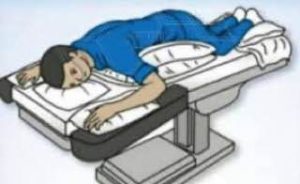
As the coronavirus pandemic progressed and patients struggled to breathe, hospitals across the world learned that very sick patients were able to breathe better when they were flipped onto their stomachs. ‘Proning’ is a medically accepted position to improve breathing comfort and oxygenation in COVID-19 patients.
This positioning, called proning (or prone-positioning), has been used for decades to improve clinical outcomes for those suffering from acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the lung condition that patients with severe COVID-19 cases develop. While proned, the patient is made to lie on his/her belly using pillows. One can also lie on their right side( right lateral), left side ( left lateral) or sit at a 60-90 degree angle in the ‘fowler position’.
If Oxygen saturation is (SpO2) drops below 94, timely proning and maintaining good ventilation can save a life. Proning improves ventilation to the lungs, and keeps the alveoli units (tiny balloon shaped structures that are the smallest passageway in the respiratory system) open, thereby easing breathing